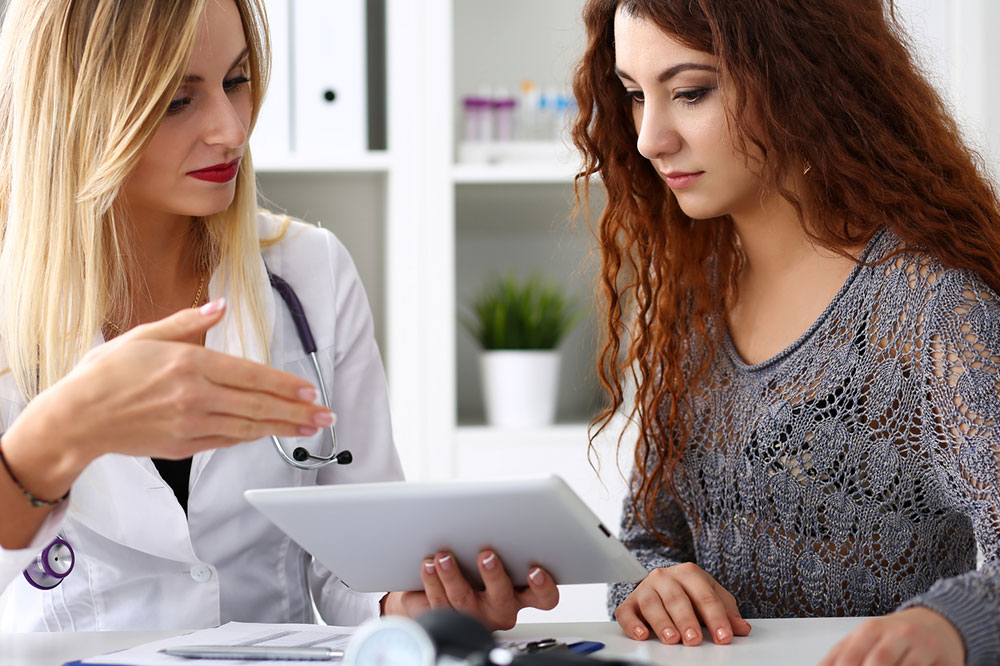
Hepatitis C – Risks and Effective Treatment Options
Hepatitis C is a disease that affects liver health and is caused by the hepatitis C virus. The symptoms can range from mild to severe and can last from a few weeks to a lifetime. The disease starts with an acute infection that generally occurs within 6 months of getting exposed to the virus. Also, if this stage remains untreated, it can lead to chronic infection and serious conditions like cirrhosis, liver damage, and cancer. Let’s look at the risk factors and treatment options for hepatitis C:
Factors that elevate hepatitis C risk
- Sharing a syringe
Hepatitis C is a blood-borne disease, so the risk of infection increases when people share needles, syringes, and any other equipment with an infected person. - Passed on to a newborn from the mother
Children born to mothers with hepatitis C face a higher risk of contracting the disease. Keeping a check on the risk factors and treatment options for hepatitis C during pregnancy is important to better manage the condition effectively. - Indulging in sexual activity with an infected partner
People with multiple sexual partners or who suffer from a Sexually Transmitted Disease (STD) like HIV have a high probability of contracting hepatitis C. - Body piercings and tattoos
A hepatitis C infection can occur if tattoos and body piercing services are undertaken using non-sterile instruments, as they may have also been used by an infected person. - People working in diagnostic labs
Health professionals working in medical units have a higher chance of contracting the infection, as they may accidentally come in contact with an infected needle.
Treatment options available for hepatitis C
- Use of antiviral pills
After taking a close look at the risk factors and treatment options for Hepatitis C, healthcare professionals may suggest antiviral medications to eliminate the virus from the body. That said, the length of the treatment and the type of medicine to be administered would solely depend on the type of hepatitis C genome present in one’s body, any underlying health issues, and their liver health. - Liver transplant
Patients with a chronic hepatitis C infection and whose liver is damaged may need to undergo a liver transplant. If the condition is not cured even after transplantation, antiviral medications are given for further treatment. - Undertake a test for liver cancer
The hepatitis virus greatly affects the liver and increases liver cancer risk. It is for this reason that taking an annual or bi-annual test for the detection of liver cancer proves helpful in early diagnosis and better management of the disease. - Vaccination
There are vaccines available for hepatitis A and B infections, and they aid in reducing the complications of chronic hepatitis C, as these two can also lead to liver damage.
There are several risk factors and treatment options for Hepatitis C, but early detection forms the key to managing the disease.